What is thiamin
Thiamin (also called vitamin B1 and Thiamine) an essential micronutrient that helps turn the food you eat into the energy you need. Thiamin is important for the growth, development, and function of the cells in your body. Specifically, thiamin is required to
- helps enzymes break down glucose
- break down amino acids
- maintain a healthy nervous system
- convert carbohydrates into energy
- support heart and muscle function
- aid in red blood cell production
Food sources of thiamin
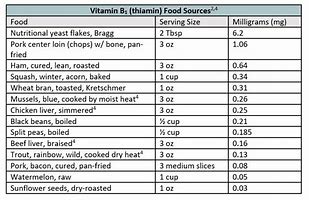
Thiamin is found in whole grains, meat and fish. Below are some food sources of thiamin.
| Food | Milligrams (mg) per serving | Percent DV* |
|---|---|---|
| Breakfast cereals, fortified with 100% of the DV for thiamin, 1 serving | 1.2 | 100 |
| Egg noodles, enriched, cooked, 1 cup | 0.5 | 42 |
| Pork chop, bone in, broiled, 3 ounces | 0.4 | 33 |
| Trout, cooked, dry heat, 3 ounces | 0.4 | 33 |
| Black beans, boiled, ½ cup | 0.4 | 33 |
| English muffin, plain, enriched, 1 | 0.3 | 25 |
| Mussels, blue, cooked, moist heat, 3 ounces | 0.3 | 25 |
| Tuna, bluefin, cooked, dry heat, 3 ounces | 0.2 | 17 |
| Macaroni, whole wheat, cooked, 1 cup | 0.2 | 17 |
| Acorn squash, cubed, baked, ½ cup | 0.2 | 17 |
| Rice, brown, long grain, not enriched, cooked, ½ cup | 0.2 | 17 |
| Rice, white, long grain, enriched, cooked, ½ cup | 0.1 | 8 |
| Bread, whole wheat, 1 slice | 0.1 | 8 |
| Orange juice, prepared from concentrate, 1 cup | 0.1 | 8 |
| Sunflower seeds, toasted, 1 ounce | 0.1 | 8 |
| Beef steak, bottom round, trimmed of fat, braised, 3 ounces | 0.1 | 8 |
| Yogurt, plain, low fat, 1 cup | 0.1 | 8 |
| Oatmeal, regular and quick, unenriched, cooked with water, ½ cup | 0.1 | 8 |
| Corn, yellow, boiled, 1 medium ear | 0.1 | 8 |
| Milk, 2%, 1 cup | 0.1 | 8 |
| Barley, pearled, cooked, 1 cup | 0.1 | 8 |
More about Ralph Teller


