Natural food nutrients offer sustainable alternatives to quality sleep 💪🏻
The National Institute of Health recently published an article on nutrients that can naturally improve sleep quality. See Nutritional Interventions for Enhancing Sleep Quality: The Role of Diet and Key Nutrients in Regulating Sleep Patterns and Disorders
The study found “nutritional interventions offer effective, sustainable alternatives for enhancing sleep quality“. The study emphasizes personalized, nutrition‐based strategies as promising, non‐pharmacological approaches for improving sleep health and managing sleep disorders. In other words, natural nutrition from whole foods can replace prescription medications (with their accompanying adverse side effects, including dependency) to achieve quality sleep,
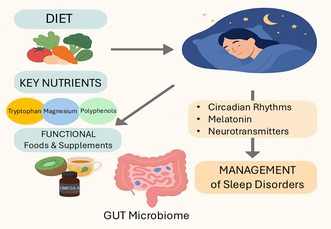
Here are some of the recommendations 😁
✅Vitamin D
Vitamin D plays an important role in the circadian rhythm regulation and aids in longer, high quality sleep. Low Vitamin D is linked to increased sleep disorders. See 8 Natural Ways to Boost Melatonin for Better Sleep. See Vitamin D Slows Cellular Aging. See Sleep, Rest and Recovery Tips. See Benefits of Eye Exposure to Sunlight. See Why Total Darkness Sleep is Best!
✅Zinc
Zinc plays a role in melatonin synthesis and is associated with improved sleep quality. See Zinc Natural Food Sources
✅Magnesium
Magnesium is critical for neurotransmitter regulation and has been associated with improvements in sleep quality and reductions in nocturnal awakenings. See Magnesium Natural Food Sources
✅Iron
Iron is also critical for neurotransmitter regulation and has been associated with improvements in sleep quality and reductions in nocturnal awakenings. See Iron Natural Food Sources
✅Carbohydrates
Diets high in carbohydrates, particularly those with a high glycemic index consumed close to bedtime, may facilitate faster sleep onset, likely due to enhanced tryptophan transport across the blood–brain barrier. A cup of milk before bedtime is a good source of carbohydrates and many other nutrients. See Raw Milk Nutrient Content.
✅Polyphenols
Polyphenols—especially flavonoids found in fruits, vegetables, and teas—exhibit antioxidative and anti‐inflammatory properties that may modulate sleep by influencing GABAergic pathways and reducing neuroinflammation
✅The Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, has been correlated with better sleep quality and reduced incidence of insomnia symptoms.
✅Chrononutrition
Chrononutrition (Chrononutrition is the study of how the timing, frequency, and composition of food intake interact with the body’s circadian system to influence metabolic and sleep–wake regulation), the timing of food intake, highlights that when we eat may be just as important as what we eat, with irregular meal timing potentially disrupting circadian alignment and impairing sleep. It’s generally recommended not to eat full meals within two hours of sleep.
✅The Gut‐Brain axis
The gut microbiota produces metabolites such as short‐chain fatty acids and neurotransmitters that can influence central sleep regulation. Dietary fibers, probiotics, and prebiotics have shown potential in modifying the gut microbiome composition in ways that favorably impact sleep quality. See Probiotics in Milk Improve Brain Function
✅Tryptophan
Tryptophan is an essential amino acid that serves as a precursor for serotonin and subsequently melatonin—two neurotransmitters fundamental to sleep onset and maintenance. Cherries are packed with melatonin, tryptophan, and powerful antioxidants, making them one of the best foods for improving sleep quality.
✅Glycine
Glycine, another amino acid, exerts sleep‐promoting effects by acting as an inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system.
✅Vitamin Bs and Serotonin
The B‐vitamin group, particularly B6, B9 (folate), and B12, plays roles in neurotransmitter metabolism. Vitamin B6 is required for the conversion of tryptophan to serotonin, while folate and B12 are involved in methylation processes that support melatonin synthesis. Deficiencies in these vitamins have been linked to sleep disturbances such as insomnia and fragmented sleep patterns. Kiwis are packed with Serotonin, folate and antioxidants.
Carlene Starck, PhD, a Metabolic Nutrition Scientist, has outstanding insight on the importance of achieving a protein quality diet. See Achieving a Protein Quality Diet
See also Chef James recommended natural food due combinations for peak performance. Natural Food Duos
Takeaway 💪🏻
Natural food nutrients offer sustainable alternatives to quality sleep.
Diet quality, functional foods, and key nutrients support sleep through neurotransmission, circadian rhythms, inflammation, and gut–brain signaling.
You’re in control!
More about Ralph Teller


